Bok Choy and Hydroponics
Growing Bok Choy hydroponically is an exciting and rewarding endeavor, offering a fresh supply of this nutritious leafy green right at your fingertips. This guide is designed to provide you with a comprehensive overview of the process, from selecting the right seeds to harvesting your crop. Whether you’re a seasoned hydroponic gardener or a beginner, understanding the specific needs and stages of Bok Choy growth will help ensure a successful and bountiful harvest.

Bok Choy in Hydroponic Systems
Bok Choy stands out as a particularly adaptable and rewarding vegetable when grown hydroponically and can be grown in just about every system. As a fast-growing leafy green, it responds well to the controlled conditions, yielding consistent, high-quality harvests in a relatively short period.
Wick Systems
Ideal for beginners, wick systems provide a low-maintenance environment for Bok Choy, using capillary action to deliver water and nutrients directly to the roots. This setup minimizes root disturbance and maintains consistent moisture levels, supporting steady growth without the need for complex equipment or monitoring.
Deep Water Culture (DWC):
In DWC systems, Bok Choy roots are suspended in nutrient-rich water, promoting rapid growth and lush leaves. Using a pump and air stone, this method ensures high oxygen levels at the roots, and is largely considered a hands-off system. However, it does require careful monitoring of water temperature and nutrient concentration.
Ebb and Flow (Flood and Drain):
Ebb and Flow systems periodically flood the root zone with nutrient solution and then drain it, offering Bok Choy an optimal balance of water, nutrients, and air. This cycle encourages strong root development but demands precise timing and control to prevent root rot or drying out.
Nutrient Film Technique (NFT):
NFT systems constantly flow a thin layer of nutrient solution over Bok Choy roots, ensuring they receive a continuous supply of water and nutrients while exposed to air. This balance promotes fast, healthy growth, but requires consistent monitoring to avoid blockages in the flow channels.

Drip System
Drip systems provide a targeted and controlled delivery of nutrient solution to Bok Choy, allowing for efficient water and nutrient use. This method supports uniform growth and is adaptable to various plant sizes, but requires regular system checks to prevent clogging and ensure even distribution.
Aeroponics:
Aeroponics offers the most advanced and efficient environment for Bok Choy, misting the roots with nutrient solution in a highly oxygenated chamber. This method encourages rapid, robust growth and minimal root disease, but demands precise control of misting intervals and nutrient strength.
Growing Conditions for Hydroponic Bok Choy
To successfully grow Bok Choy in a hydroponic system, it’s crucial to create the right growing conditions that cater to its needs. Understanding the ideal pH levels, spacing, germination requirements, and other environmental factors is key to nurturing healthy, vibrant Bok Choy plants.
pH
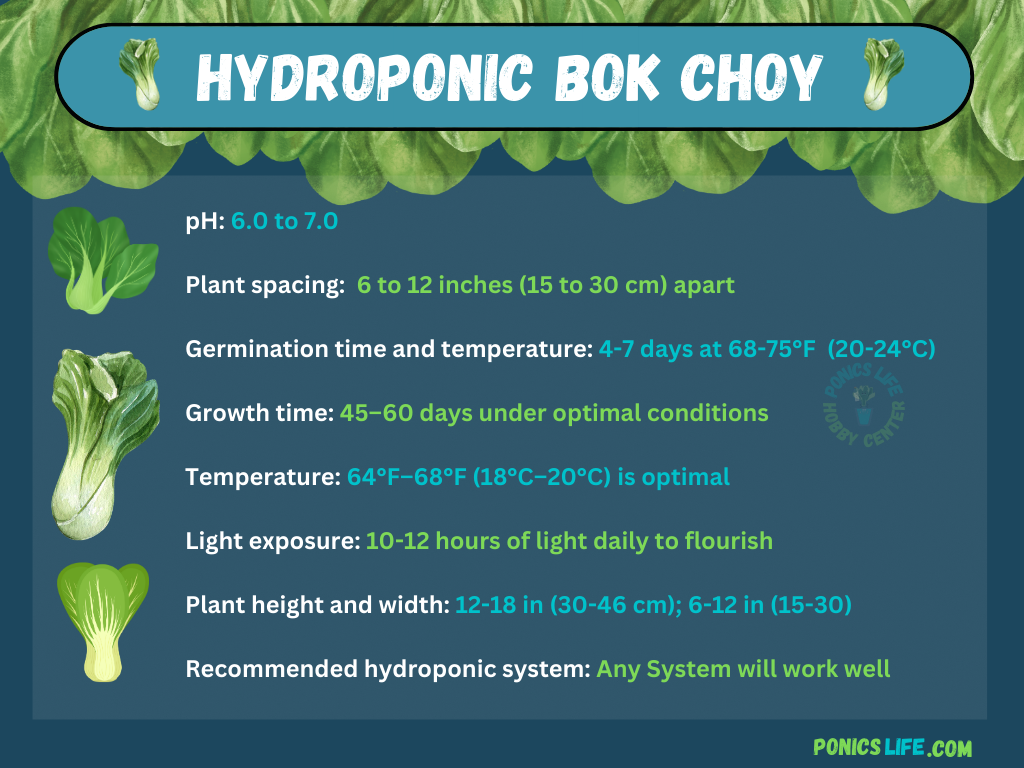
Bok Choy thrives in a slightly acidic to neutral pH range, ideally between 6.0 and 7.0. Maintaining this pH range in your hydroponic system ensures optimal nutrient uptake and prevents issues like nutrient lockout, which is crucial for healthy growth and development.
Spacing
When planting Bok Choy hydroponically, allow about 6 to 12 inches between each plant. This spacing ensures adequate room for growth and air circulation, minimizing the risk of disease and competition for nutrients and light.
Germination and Germination Temperature
Bok Choy seeds typically germinate within 4 to 7 days when kept at a consistent temperature of 50-80°F (10-27°C), although 68-75°F (20-24°C) is ideal. A stable, warm environment speeds up germination and results in a higher success rate.
Time to Maturity
Bok Choy generally reaches maturity in about 45 to 60 days after planting in a hydroponic system. This quick turnaround makes it an ideal choice for gardeners looking for fast harvests.
Temperature
For optimal growth, maintain the ambient temperature around Bok Choy between 64°F–68°F (18°C–20°C). And although Bok Choy can tolerate temperatures as high as 95°F (35°C) and as low as 27°F (-3°C), extreme temperatures can stunt growth or cause bolting (premature flowering), so consistent temperature control is key.
Light Exposure
Bok Choy requires 10-12 hours of light daily to flourish. In hydroponic systems, using grow lights can provide the necessary light intensity and duration, especially in settings with limited natural light.
Plant Width and Height
Hydroponically grown Bok Choy typically reaches a height of 12 to 18 inches and spreads about 6 to 12 inches (although spreading to 18 inches isn’t uncommon). This compact size makes it suitable for most hydroponic systems, even those with limited space.
Recommended Hydroponic System
Bok Choy grows well in almost all hydroponic systems, including wick, deep water culture, NFT, and aeroponics. Each system has its advantages, but Bok Choy’s adaptability makes it a reliable crop for both beginners and experienced hydroponic gardeners.
How to Start Bok Choy
Selecting the right seeds and understanding the best conditions for germination is a key step for growing Bok Choy hydroponically. These early stages are crucial for establishing a healthy, productive crop of this versatile leafy green.
Selecting Seeds
When selecting Bok Choy seeds for hydroponics, always go for quality. Prioritize seeds from trusted suppliers with a good track record for germination and vigor, as these characteristics are important for successful hydroponic cultivation.
Sowing Seeds Indoors
Start Bok Choy seeds indoors in a soilless medium (see our big list of hydroponic mediums) or starter plugs, keeping them moist but not waterlogged. Provide a warm environment, ideally around 68-75°F (20-24°C), and slowly expose them to more light after sprouting, either from a grow light or a sunny windowsill, to encourage strong, healthy seedling growth.
Sowing Seeds Outdoors
If you’re initiating Bok Choy seeds outdoors for eventual hydroponic transfer (whether outdoor or indoor), it’s crucial to sow at the right time, typically in early spring or late summer, to avoid extreme temperatures. Outdoor germination subjects the seeds to natural environmental conditions, so ensure consistent moisture and protection from harsh elements.
How to Grow Bok Choy
Successfully growing Bok Choy in hydroponic systems involves navigating various stages, from transplanting to pest management. Each stage requires specific care and attention to ensure the healthy development and abundant harvests of this leafy green.

Transplanting
Transplant Bok Choy seedlings into your hydroponic system when they have developed 2-3 true leaves, a tell-tale sign they are strong enough for the transition. Handle the roots with care to minimize stress and plant them at the same depth as they were growing previously. After transplanting, ensure consistent light and temperature to help the plants adjust smoothly to their new environment.
Pruning
Pruning is generally not required for Bok Choy in hydroponics, but removing any yellow or damaged leaves can help maintain plant health. This helps in focusing the plant’s energy on growing healthy leaves.
Harvesting
Bok Choy can be harvested when it reaches a size you desire, typically 4-6 weeks after transplanting. Cut the main stem at the base to harvest the whole plant (most common way), or pick individual outer leaves for a continuous harvest, allowing the center leaves to grow.
Disease Prevention
Vigilant monitoring is essential in hydroponic systems to prevent diseases in Bok Choy, as pathogens can quickly spread from plants touching or in their shared water supply. Regularly check for signs of disease, such as discolored leaves or stunted growth, and maintain a clean system by replacing water and cleaning equipment periodically.
Plant Support
While Bok Choy generally doesn’t require structural support in hydroponic systems (such as using a trellis for tomatoes), ensuring stable and adequate support for the growing medium and root structure is important. For larger or top-heavy plants, consider using small stakes or ties to maintain upright growth and prevent any bending or breaking of stems and leaves.
Pest Management
Monitor your Bok Choy for common pests like aphids and caterpillars. In hydroponic systems, managing pests often involves physical removal, introducing beneficial insects, or using organic, hydroponic-friendly pesticides to avoid contaminating the water system.
How to Harvest Bok Choy
Harvesting Bok Choy from a hydroponic system involves timing and techniques that maximize both yield and freshness. Knowing when and how to harvest, as well as the best practices for post-harvest storage, are key steps to enjoying your hydroponically grown Bok Choy at its best.
When to Harvest
Bok Choy is ready to harvest in hydroponic systems typically between 4 to 6 weeks after transplanting, when the leaves are lush and the plant has reached a desirable size (this is typically the 10–15 leaf stage). The best indicator is the maturity of the leaves, which should be crisp and vibrant. Harvesting at the right time ensures the best flavor and nutritional value.
How to Harvest
To harvest Bok Choy, use a clean, sharp knife to cut the main stem at the base of the plant, which allows for harvesting the entire plant at once. Alternatively, for a continuous harvest, you can pick individual outer leaves, leaving the center leaves to continue growing. After harvesting, wash the leaves thoroughly to remove any residual nutrient solution.
After Harvesting
Once harvested, Bok Choy can remain fresh for about 1 to 2 days at room temperature. For longer storage, refrigerating the Bok Choy at around 39°F (4°C) can extend its freshness to over 5 days.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Here are some frequently asked questions that you might encounter as you start growing Bok Choy in a hydroponic system.
What other names does Bok Choy Have?
Bok Choy has several different names depending on where you are and who you’re talking to. The most common names for it are Bok Choy and Pak Choi but it is also sometimes referred to as Chinese Mustard, Celery Mustard, Pe-tsai, Pak Choy, Bok Choi, chongee, and Japanese white celery mustard, among others.
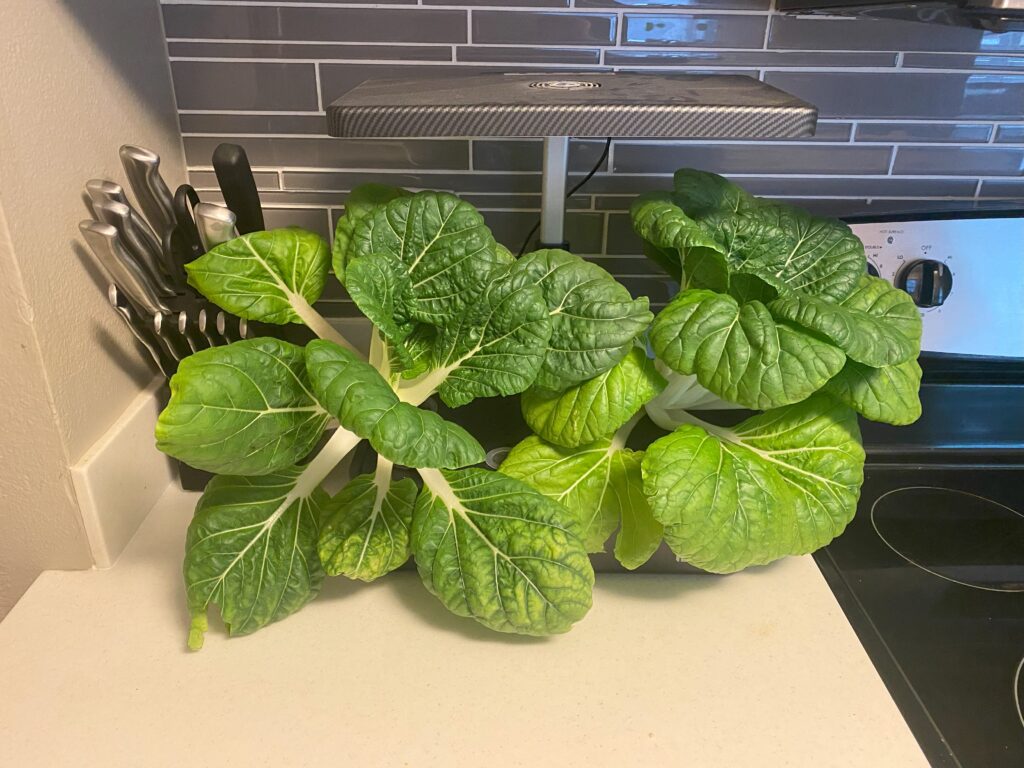
Are Nutrient Deficiencies Common?
Hydroponics is a trial and error hobby and if you’re just starting out, you’re probably going to have some nutrient issues. Make sure to continually monitor your plant and look for any abnormalities. Pictured below is two Bok Choy plants growing in a countertop garden. While the inner leaves are dark green, the outer leaves are much lighter, a clear sign that something may need to be adjusted.

Can I regrow Bok Choy from cuttings in a hydroponic system?
Yes, it is possible to regrow Bok Choy from cuttings. One method is to place the base of the stem in water until roots develop, and then transfer it to your hydroponic setup.
Do I need to use grow lights for hydroponic Bok Choy, or is natural light sufficient?
While natural sunlight is sufficient when growing outdoors, you need to use grow lights when growing indoors. You can try using a window if enough light is able to make it through but it will be difficult.
How often should I change the nutrient solution for Bok Choy in hydroponics?
It’s advisable to change the nutrient solution every 2 to 3 weeks, but this can vary based on the system and plant needs and most hobbyists will just top their water off. Regularly check the nutrient levels and pH.
Can I grow Bok Choy hydroponically year-round?
Yes, one of the advantages of hydroponic systems is the ability to control growing conditions (if growing indoors), allowing for year-round cultivation of Bok Choy.
What is the best hydroponic system for growing Bok Choy?
As described above, Bok Choy grows well in most systems, but Deep Water Culture and Nutrient Film Technique are popular choices for their simplicity and effectiveness. Read our Types of Hydroponic Systems Guide to learn more.
Is it ok to use plastic to grow Bok Choy?
Yes, it is perfectly safe as long as you’re following Food Grade Safe standards.






